The animation works at two levels
- macro and micro
At macro level it gives an insight into structure and
design of a pressure cooker, its parts and their description;
its advantages, principle of working etc.
At micro level it explains
the concept of boiling and how molecule interact with each
other to create "pressure". The mechanism of boiling
in an open pan, closed pan and further explanation based
on momentum. Bonds in water and how are they affected
by energy.
It links observed phenomenon
to unseen molecules, it correlates
- Boiling ----Molecular bonds & their energies
- Pressure ---- Collision of molecules --- Conservation
of momentum
- Bubbles formation in boiling --- Vapour molecules of
water
- Heat --- Energy transfer between flame, metal atoms
and water molecules
- Atmospheric pressure --- Effect of gravity
- Effect of atmospheric pressure --- Collision of air
molecules.
The detail of the content covered
and questions answered in animation format and in our explanatory
notes are as follows:
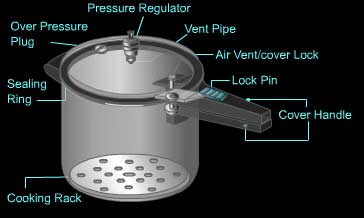
Pressure cooker
- Principle
- Design
- Methods of release of pressure ( in EN)
- Parts
- History ( in EN)
- Safety feature ( in EN)
- Benefits ( in EN)
- Materials used in the manufacturing ( in EN)
- What is happening inside it when water is heated ?
- Why does the temperature increase faster in a cooker
than in an open pan?
- Pressure cooker an application of Gay lussac's law
- As the pressure goes on increasing, the temperature
also rises faster (why)
- How does superheated steam ensure faster and better
cooking ?
- Why boiling point of water changes due to pressure ?
- based on change in molecular structure of water
- Mechanism of boiling in open pan - based on inter molecular
forces - energy exchange between metal & water - collision
- momentum - kinetic energy correlation
- Why do the H2O molecules that have broken free start
rising to the top ?
- Why does boiling take place when vapour pressure = atmospheric
pressure ?
- What has kinetic energy and collisions got to do with
it ?
- Does boiling take place only at the surface of liquid?
- Complete story told in step-by-step of what happens
to the molecules, energy and collisions as the temperature
graphs rises from 27--80--100 --100+
- How do air molecules exert pressure on the water vapour
?
- Do the bubbles formed in boiling at the base contain
air ?
- How is boiling affected in a closed pan ? - Pressure
changes
- Why boiling point increases in a closed pan ? - water
vapour molecules
- Equilibrium state in closed pan
- Temperature - pressure relationship under constant volume.
- Generation of high pressure inside pressure cooker -
complete explanation done on the basis of momentum, collisions,
Newton second law of motion and conservation of momentum.
- Momentum explained by an example
- Why pressure goes up when more gas is added to a closed
container ?
- what would happen if the walls of a cooker are made
up of thinner material ?
- why pressure cooker is a boon to those living at high
altitudes?
- Why Boiling point decreases with an increase in altitude
? Why atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude ? what
it has to do with gravity ?
- How can water boil at room temperature?
Case 1) heat at definite pressure
Case 2) reducing pressure
- Why is steam so efficient in cooking? ( in EN)
- Superheating water allowing it not to boil till 118
deg C under normal conditions.( in EN)
- Nucleation ( in EN)
- Exploding water ( in EN)
- Difficulty in boiling water in microwave oven ( in EN)
- Superheating water on a ordinary stove ( in EN)
- Why does water boil when a solid is introduced in it
? ( in EN)
( EN = Explanatory notes)
|

