Brain cell (neuron)
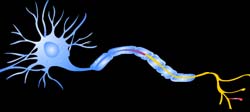
The human brain contains more than 100 billion brain cells
called nerve cells or neurons. All neurons have same basc
structure. Many number of nerves cells together are called
nerve. Nerve is a pale, tough and string like structure
and acts as a living telephone wire.
A neuron is a long cell that has a thick central area containing
the nucleus; it also has one long structure called an axon
and one or more short, bushy structures called dendrites.
Dendrites receive impulses from other neurons. These impulses
propagate electrically along the cell membrane to the end
of the axon. At the tip of the axon the signal is chemically
transmitted to an adjacent neuron or muscle cell.
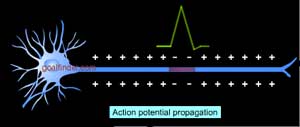
When the electrical signal (action potential) reaches the
tip of an axon, it stimulates small presynaptic vesicles
in the cell.
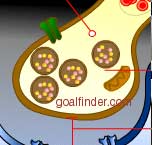
These vesicles contain chemicals called neurotransmitters,
which are released into the microscopic space between neurons
(the synaptic cleft). The neurotransmitters is attached
to specialized receptors on the surface of the adjacent
neuron. This stimulus causes the adjacent cell to depolarize
and propagate an action potential of its own. The duration
of a stimulus from a neurotransmitter is limited by the
breakdown of the chemicals in the synaptic cleft and the
re-uptake by the neuron that produced them. Formerly, each
neuron was thought to make only one transmitter, but recent
studies have shown that some cells make two or more.
|

